The following insight is derived from a recent ‘Assembly’ event featuring Prof. Suraj Srinivasan, Valerie Legat, and Fernando Alvarez, on the topic of The Eco-Digital Era: The Dual Transition to A Sustainable & Digital Economy.
Meet Our Guest Contributors:
Suraj Srinivasan | Professor of Business Administration at Harvard Business School

Dr. Srinivasan’s research and teaching practicum examines the intricate workings of corporate governance in the U.S. and internationally. As a leading academic and practitioner, Dr. Srinivasan has extensively studied globally pressing issues like the impact of globalization on corporate disclosure practices, the effect of securities regulation on incentives of U.S.-based companies, and reputational consequences for corporate directors when companies experience financial reporting problems.
For more information, please visit Dr. Srinivasan’s faculty profile at Harvard Business School.
Valerie Legat | Managing Director & Head of Digital at Astorg

Valerie has more than 25 years of experience in innovation, entrepreneurship, and digital transformation. Valerie leads multi-disciplinary teams of business strategists, designers, and technologists to support CEOs in their digital agenda, by focusing on helping teams build capabilities to re-invent business models and rapidly launch transformational digital services and products. In addition to working for some of the biggest multi-national corporations including McKinsey & Company and Carrefour, Valerie is a former founder of a digital agency startup (Business Lab) that she managed for 18 years.
For more information, please visit Valerie’s LinkedIn profile.
Fernando Alvarez | Group Chief Strategy & Development Officer at Capgemini

Fernando leads Capgemini’s global efforts in corporate strategy, mergers, and acquisitions focusing on group partnerships and strategic initiatives. Fernando has over 30 years of experience in business, most of which were spent in executive roles at Capgemini such as Global Head of Capgemini’s Mobile Solutions Service Line, and Group Chief of Global Strategic Initiatives and Partnerships. Fernando’s thought and practical leadership have propelled Capgemini to global imminence in the space of digital initiatives.
For more information, please visit Fernando’s LinkedIn profile.
Introduction: Why does this matter?
The digital and sustainability paths, previously considered to be parallel, are now highly intersecting and reinforcing each other, pointing towards a symbiotic relationship between technological advancement and environmental values. Showcasing this relationship, digital technologies are expected to contribute more than one-fifth, and up to one-third, of the GHG emissions reduction required by the Paris Agreement by 2030, illustrating their importance to sustainability transformation. As such, it’s important to understand the main drivers of this shift because of the implications this shift has on the global business landscape, including the demand for businesses to prioritize integrating digital innovation with sustainable practices. With the eco-digital economy including benefits that extend well beyond improvement in core business activities, it’s imperative for leaders to have a vision for digital transformation at their organizations going forward with a focus on harnessing the opportunities created by the emerging eco-digital economy including digital strategy, cybersecurity, sustainability, and more.
This Capgemini Research Institute report, The Eco-Digital EraTM: The dual transition to a sustainable and digital economy, developed in collaboration with the Digital Value Lab at the Digital Data Design Institute at Harvard, delves in-depth into the digital economy and how, in addition to its business benefits, it has the potential to provide significant environmental and social value.
The Problem: What is the research question, and what specific problem does it attempt to answer?
This collaborative research study set out to understand the nature of the emerging eco-digital economy and its potential to drive economic, environmental and social values for businesses and society at large. The following questions helped orient the general approach of the research study:
- What does the eco-digital economy look like, and what sets it apart from the traditional digital economy it is replacing?
- What are the main drivers of the growth of the eco-digital economy?
- In what ways does the eco-digital economy contribute to global GDP?
- How can businesses leverage this new space to experiment with and scale new models, in order to create economies of scale and new revenue streams?
- And perhaps the most important question in this study—how do the spaces of digital and sustainability overlap and how are they able to work symbiotically?
In search of answers to these key questions, the researchers carried out 1,500 surveys involving incumbents and startups from 14 different countries. These surveys were complemented with in-depth, follow-on interviews with 26 senior industry executives and experts.
The Solution and Impact: What are the key findings of this research, and what solutions do these findings point to?
The world is experiencing a dual transition towards a more digital and sustainable future. We call it the ‘Eco-Digital Era’.
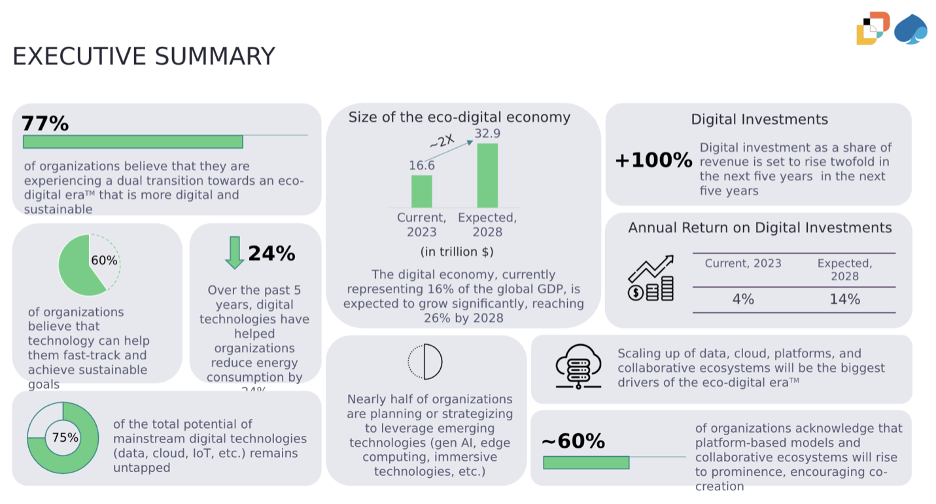
Overall, the findings of this research study point to the imminence of a dual space. Organizations recognize the symbiotic relationship between these two transitions, emphasizing that advancements in technology are crucial for achieving sustainability goals. A significant portion of organizations surveyed (8 out of 10) reinforced the belief in a dual transition. These organizations report that digital technologies have enabled them to reduce their energy consumption by a quarter, highlighting the positive impact of digitalization on sustainability.
Another key takeaway is the projected exponential growth of the digital economy within the next five years—with a predicted doubling in size, as a result of the emergence of this dual space. This growth is not just limited to certain geographical areas but is a global phenomenon, indicating widespread acceptance and integration of digital technologies across various sectors. Despite the rapid advancements, it’s believed that only 25% of the potential of digital technologies has been realized, suggesting that there is still significant room for growth and innovation in this field. Speaking of this predicted exponential growth, this research study shows this growth to predominantly be driven by scaling existing technologies such as data analytics, cloud computing, IoT, RPA, AI, and machine learning rather than from emerging technologies. This implies that the focus is and should be on leveraging and expanding the technologies that organizations already have in place.
From a strategy point of view, the findings of this research reaffirm the fact that digital and sustainability efforts are increasingly being integrated at a strategic level. This has and will continue to increase the appeal of circular business models and other innovative approaches that are both sustainable and economically viable. Regulatory forces are predicted to drive the adoption of more sustainable and digital practices, which is indicative of the crucial role legislative frameworks can play in accelerating the transition towards an eco-digital era.
Implications for Policy and Practice: What are the broader implications of this research study for policy and practice, and what could be done to mitigate negative impacts and to augment positive outcomes?
On harnessing the opportunities of an Eco-Digital era
Any major innovation brings with it challenges which should be viewed not as obstacles but as opportunities for growth. The takeaways of this research study advocate for a forward-thinking approach that sees digital transformation as an enabler for achieving sustainability goals. To thrive in the eco-digital era, organizations need to prioritize strategic alignment, resource allocation, and the cultivation of a skilled and adaptable workforce. For example, it’s crucial for organizations to align their goals and objectives with digital initiatives. This may require them to prioritize investments in reskilling their workforce, automating business processes, and ensuring that robust cybersecurity and privacy protocols are put in place. This reflects a balanced approach to embracing digital transformation while addressing potential risks and challenges.
In addition to a focus on digital initiatives, a holistic approach that integrates strategy and operations is recommended, with digital technologies poised to play a key role in sustainability efforts. Collaboration through platforms, ecosystems, and partnerships is essential since no single entity can tackle all challenges alone. An important aspect of this collaboration will be about meaningfully contributing to the growing convergence of digital innovation and sustainability efforts. The environmental impact of digital technologies, particularly in terms of energy consumption and GHG emissions is substantial. As such, leveraging digital technologies to accelerate sustainability goals while being mindful of the environmental impact of digital solutions themselves is paramount towards achieving a net positive outcome.
Q&A Highlights from the Live Event
How can companies adapt their business models to sustainability regulations and use technologies to automate their sustainable reporting process?
Leveraging digital technologies companies can embrace sustainable business models, such as circular and as-a-service models more easily. Aligning their digital initiatives with sustainability goals leads to the development of eco-friendly technologies, such as energy-efficient data centers and smart grids, contributing to both environmental sustainability and digital progress.
Generative AI tools are now available to integrate with operations to aid sustainable reporting. Solutions provided by C3 AI, a US-based startup, demonstrate how generative AI can unify and manage diverse ESG data, automating the reporting process and making it more efficient for teams to refine and verify the accuracy of reports.
Could an eco-digital economy provide a tailwind to help lower inflation on a macro-level?
In the eco-digital economy, the scaled implementation of digital technologies will lead to increased efficiency in various sectors. Technologies can optimize resource use, streamline supply chains, drive innovation, and reduce waste, thereby contributing to cost savings. This optimization can potentially result in lower prices for goods and services, positively impacting inflation rates. As environmentally friendly practices become more prominent, consumer preferences may shift towards sustainable products and services. Businesses responding to these preferences may find cost-effective solutions, potentially mitigating inflationary pressures. Government policies and regulations that encourage eco-friendly practices may provide incentives for businesses to adopt sustainable technologies. This regulatory push may also lead to cost efficiencies and influence inflation rates.
While the potential for cost savings and efficiency gains exists, the specific macroeconomic effects would be contingent on the scale and speed of the adoption of digital technologies, regulatory frameworks, and the broader economic context. Therefore, the implications of an eco-digital economy on inflation would depend on the interplay of various such factors.
Will digital projects qualified as accelerators for sustainable transition compensate for the “non sustainable” ones?
Yes, digital footprints are poised to expand with the widespread adoption of established and emerging technologies. However, harnessing technologies to reduce the carbon footprint, coupled with advances in energy efficiency within the digital landscape, suggest that environmental benefits of scaling digital technologies are expected to outweigh their environmental costs, affirming the significant positive impact of digital technologies. A notable case is LG Electronics in Changwon, South Korea, achieving a 17% productivity boost, 70% higher product quality, while also reducing energy consumption by 30% by converting its assembly-line simulation into a digital twin, integrated with real-time data.
How can our physical presence on earth and sustainability efforts be complimentary? Is tech the only way to address sustainability issues, or can something be done “on the ground” as well?
Addressing the carbon impact of life and promoting sustainability doesn’t solely rely on technology; on-ground initiatives also play a crucial role. Especially at an individual level, making sustainable choices, such as opting for products/services with minimal environmental impact, minimizing waste through local recycling programs, and educating communities on waste management, as well as supporting local businesses to reduce transportation, can significantly contribute to sustainability.
As Valérie Legat pointed out in the webinar, data and technology play a pivotal role in Carrefour’s sustainability efforts. For instance, during e-commerce checkout, customers can view the carbon footprints of their chosen items and receive suggestions for alternative, environmentally friendly baskets. Additionally, when customers select their preferred delivery slots, the system recommends ecologically favorable (‘green’) slots. Opting for slots coinciding with existing deliveries in the vicinity reduces overall emissions. Raising awareness about such initiatives and actively supporting and participating in them can create a larger impact.
At an organizational level, technology facilitates large-scale initiatives and programs, making them more efficient and impactful. However, individual actions and community engagement remain integral to achieving a sustainable balance between life and environmental well-being.
What is being done to mitigate the energy consumption problem created by cloud-based technologies? Are there organizations working on frameworks for transparent sustainability and consumption KPIs on a national, regional, or global level?
We acknowledge the concern that the reduction in energy consumption by organizations leveraging cloud technologies might be offset by the increased energy consumption of cloud providers. Our analysis suggests that through optimal integration of digital technologies, organizations can achieve net reduction in emissions or energy consumption. We have provided details regarding the calculations and sources in the dedicated sub-section titled “Digital technologies contribute more to reducing emissions than their own carbon footprint” within our report, which can be accessed here: https://www.capgemini.com/insights/research-library/the-new-digital-economy-research/
Historically, even as compute and storage demand from data centers has grown exponentially, the energy consumption of cloud computing has increased only marginally. A study revealed that, while computing in data centers surged by around 550% from 2010 to 2018, energy consumption increased by a mere 6% during this period. Remarkably, despite exponential growth in cloud computing demand, data centers consumed around 1% of the world’s electricity output in 2018, the same as in 2010. Most of the large cloud providers are already taking steps to mitigate their carbon footprint. Microsoft Azure, for instance, is already carbon-neutral since 2012. In 2022, 90% of the electricity consumed by Amazon was attributable to renewable energy sources.
Moreover, several global organizations have established frameworks, standards, and platforms to guide sustainability and integrated reporting. CDP, the Climate Disclosure Standards Board (CDSB), the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC), and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) are some of the internationally recognized entities setting standards for sustainability reporting.
