Originally published in The Harvard Gazette.
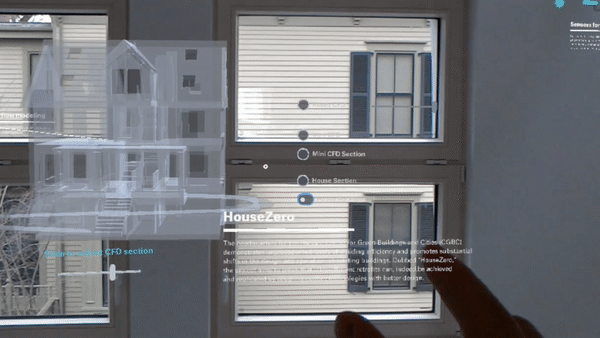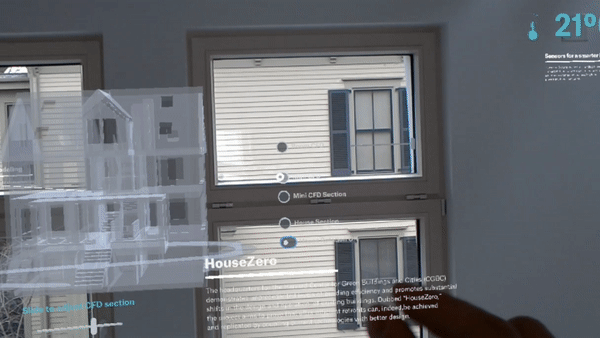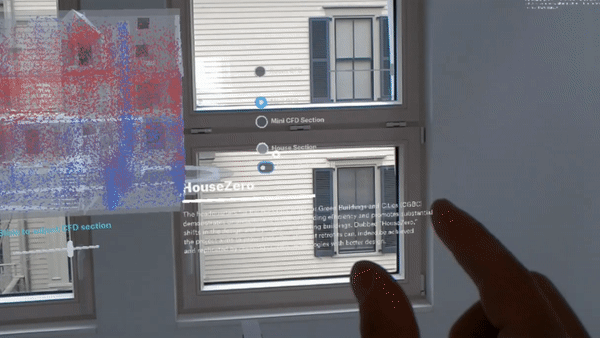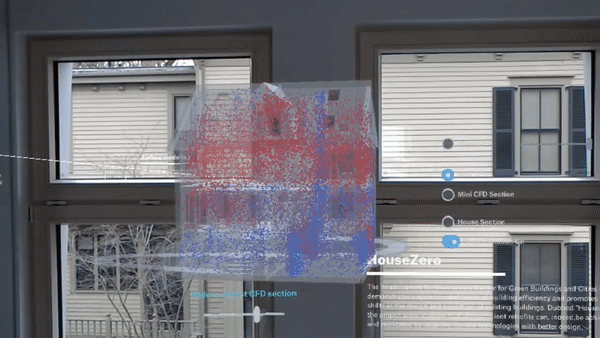
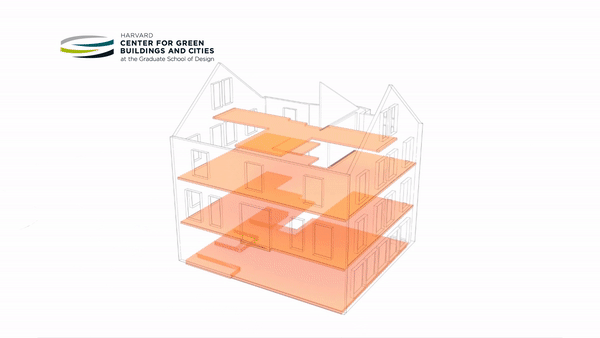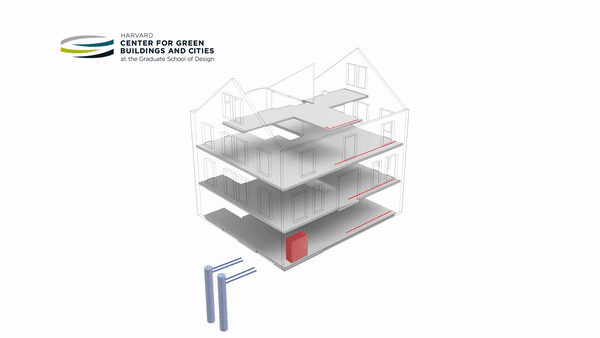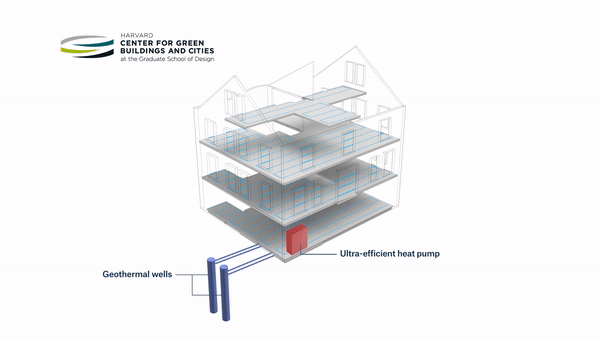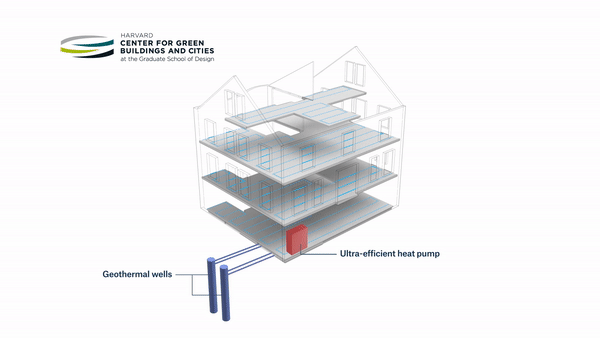
An ambitious retrofit of a pre-1940s building on Harvard’s campus into a living laboratory and energy-positive prototype for ultra-efficiency has opened its doors. HouseZero is intended to address one of the biggest energy problems in the world today — inefficient existing buildings. Its design was driven by the goals of nearly zero energy for heating and cooling, zero electric lighting during the day, operating with 100 percent natural ventilation, and producing zero carbon emissions. The building is intended to produce more energy over its lifetime than was used to renovate it and throughout its subsequent operation.
Leveraging the renovated building as both a workspace and a research tool, the Harvard Center for Green Buildings and Cities (CGBC) will use millions of data points from hundreds of sensors to continually monitor its performance. This data will fuel research involving computational simulation, helping the center develop new systems and data-driven learning algorithms that promote energy-efficiency, health, and sustainability.






“HouseZero’s flexible, data-driven infrastructure will allow us to conduct further research that demystifies building behavior, and design the next generation of ultra-efficient structures,” said Ali Malkawi, founding director of CGBC and the creator and leader of the HouseZero project.
The new space will also be used to research how to fundamentally redefine how a structure can connect with and respond to its natural environment to promote efficiency and health. Rather than approaching the building as a “sealed box,” the building envelope and materials of HouseZero were designed to interact with the seasons and the exterior environment in a more natural way. The building will adjust itself constantly — sometimes by the minute — to reach thermal comfort for its occupants.
“HouseZero challenged us to rethink the conventions of building design and operation to enhance lifelong efficiency and quality of life for occupants,” said Malkawi.