ZARA: Achieving the “Fast” in Fast Fashion through Analytics

How does fast fashion make any business sense? Zara uses intensive data and analytics to manage a tight supply chain and give customers exactly what they want.
Introduction
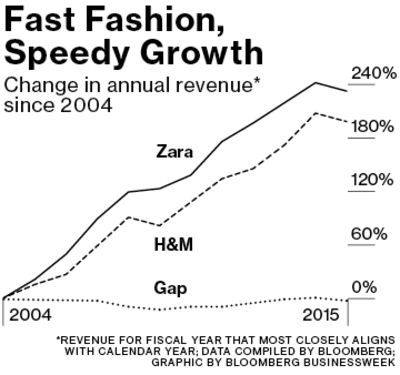
Zara’s parent company Inditex has managed to thrive in the last decade while several other fashion retailers have faced declining sales or stagnant growth. Inditex has grown over 220% in annual revenue since 2004, more than its key competitors like H&M, Gap, or Banana Republic (1).
The value of a fast fashion brand is to bring the latest designs and “trendiest trends” into the market as quickly as possible, preferably as soon as they became hot on the catwalk, and to provide these at a reasonable price. The traditional fashion industry is not well equipped to provide such value as it operates on a bi-annual or seasonal basis, with long production lead times due to outsourced manufacturing to low cost-centers. Zara has turned the industry on its head by using data and analytics to track demand on a real-time, localized basis and push new inventory in response to customer pull. This enables them to manage one of the most efficient supply chains in the fashion industry, and to create the fast fashion category as a market leader.
How Zara Uses Data
Inditex is a mammoth retailer, producing over 840 million garments in a year, the majority of which are sold by Zara (2). Every item of clothing is tagged with an RFID microchip before it leaves a centralized warehouse, which enables them to track that piece of inventory until it is sold to a customer (3). The data about the sale of each SKU, inventory levels in each store, and the speed at which a particular SKU moves from the shelf to the POS is sent on a real time basis to Inditex’s central data processing center (see picture below). This center is open 24 hours a day and collects information from all 6000+ Inditex stores across 80+ countries and is used by teams for inventory management, distribution, design and customer service improvements (4).
Zara’s Data Processing Center receives real-time data from around the world (4).
When the apparel arrives in store, RFID enables the stockist to determine which items need replenishing and where they are located, which has made their inventory and stock takes 80% faster than before (3). If a customer needs a particular SKU, salespeople are able to serve them better by locating it immediately in store or at a nearby location. Moreover, every Zara location receives inventory replenishments twice a week, which is tailored to that stores real-time updates on SKU-level inventory data.
The sales tracking data is critical in enabling Zara to serve its customers with trends that they actually want, and eliminate designs that don’t have customer pull. Zara’s design team is an egalitarian team of over 350 designers that use inspiration from the catwalk to design apparel on daily basis. Every morning, they dive through the sales data from stores across the world to determine what items are selling and accordingly tailor their designs that day. They also receive qualitative feedback from empowered sales employees that send in feedback and customer sentiment on a daily basis to the central HQ e.g., “customers don’t like the zipper” or “she wishes it was longer” (1).
At the start of the planning process, Zara orders very small batches of any given design from their manufacturers (even just 4-6 of a shirt per store). The majority of Zara’s factories are located proximally in Europe and North Africa, enabling them to manufacture new designs close to home and ship them to their stores within 2-3 weeks. They then test these designs in store, and if the data suggests the designs take off, Zara can quickly order more inventory in the right sizes, in the locations that demanded it. Such store-level data allows Zara to be hyper-local in serving their customer’s needs – as tastes can vary on a neighborhood level. As Inditex’s communication director told the New York Times,
“Neighborhoods share trends more than countries do. For example, the store on Fifth Avenue in Midtown New York is more similar to the store in Ginza, Tokyo, which is an elegant area that’s also touristic. And SoHo is closer to Shibuya, which is very trendy and young.” (5)
Unlike other retailers that may order inventory based on their hypotheses about tastes at a regional level, Zara is tailors its collections based on the exact zip code and demographic that a given location serves (5).
Zara’s Results vs. Competitors
Zara sells over 11,000 distinct items per year versus its competitors that carry 2,000 to 4,000. However Zara also boasts the lowest year-end inventory levels in the fashion industry. This lean working capital management offsets their higher production costs and enables them to boast rapid sales turnover rates.
At Zara, only 15% to 25% of a line is designed ahead of the season, and over 50% of items are designed and manufactured in the middle of a season based on what becomes popular (2). This is in direct contrast to a close competitor like H&M where 80% of designs are made ahead of the season, and 20% is done in real-time during the season (6). Most other retailers commit 100% of their designs ahead of a season, and are often left with excess inventory that they then have to discount heavily at season-end. Instead, Zara’s quick replenishment cycles create a sense of scarcity which might actually generate more demand:
“With Zara, you know that if you don’t buy it, right then and there, within 11 days the entire stock will change. You buy it now or never.” (5)
Sources:
- https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-11-23/zara-s-recipe-for-success-more-data-fewer-bosses
- http://www.digitalistmag.com/digital-supply-networks/2016/03/30/zaras-agile-supply-chain-is-source-of-competitive-advantage-04083335
- http://static.inditex.com/annual_report_2015/en/our-priorities/innovation-in-customer-services.php
- http://www.refinery29.com/2016/02/102423/zara-facts?utm_campaign=160322-zara-secrets&utm_content=everywhere&utm_medium=editorial&utm_source=email#slide-11
- http://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/11/magazine/how-zara-grew-into-the-worlds-largest-fashion-retailer.html?pagewanted=all
- https://erply.com/in-the-success-stories-of-hm-zara-ikea-and-walmart-luck-is-not-a-key-factor/




Great post Ravneet – I had never read about Zara’s extremely quick supply chain or hyper-local testing. I have a question for you about fast fashion in general, but especially for Zara since it produces and sells more distinct items than its competitors: it seems that many designers are not fond of the “runway-inspired” fashions sold at these stores and some have even sued stores for copying their designs. Do you think Zara and other brands like it are doing anything wrong, and if not, what recourse do designers have for “imitations” of their work?
Thanks for the post Ravneet. Zara and H&M are beacons of hope for a mostly distressed industry. Do you think Zara’s advantage could be sustained in the event of a full-on assault by the Amazons of the world?