Nike: Leading Innovation and Sustainability

As a company that built one of the most iconic brands aimed to “bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete in the world,” Nike’s innovation stretches beyond product functionality and aims for sustainability. Nike has made significant strides innovating in materials, manufacturing and supply chain operations. What should they do next?
Challenges Faced
Nike’s operating model is based on outsourcing the manufacturing to low-cost factories around the globe to support their worldwide demand.[1] This geographically dispersed model leaves the company vulnerable to climate change. Flooding has already caused factories to close and threatened the harvest of cotton.[2] As extreme weather events become more common, reliance on traditional agricultural raw materials may leave Nike constrained.
In addition to supply chain issues, materials and methods of manufacturing apparel have significant environmental impacts. A $1.8 trillion market, 40% of apparel products are from cotton, wool and other agriculture products. 60% of the products are from polyester, nylon and other petroleum based synthetics, which have environmental consequences.[3] Additionally, 400 gallons of water are needed to produce one pound of textiles.[4] Recognizing the environmental impact, Nike is working to innovate in these areas.
Material Innovations
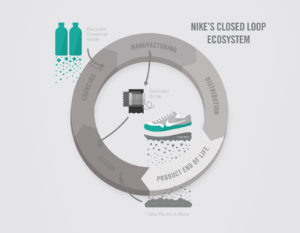
The first way Nike is improving the sustainability of its business is through the products it is producing. The Chief Sustainability Officer, Hannah Jones, aims to have a 100% renewable system with “an entirely closed-loop business model.”[5] Nike is making significant strides by offering new materials that increase performance, while reducing the environmental footprint. The Flyknit shoe line is one of the newest products, which uses recycled polyester instead of traditional materials to reduce waste by 80%, or “3.5 million pounds of waste and […] diverting 182 million bottles from landfills.”[6] Flyknit is a step towards decreasing Nike’s climate vulnerability by reducing its reliance on agricultural raw materials such as cotton. Even with the sustainability upside, Nike did not sacrifice functionality, as the Flyknit line enhances performance by expanding to the athlete’s foot. Moving forward, Nike continues to look for innovation in new places. In conjunction with Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) CoLab, Nike is using crowd-sourcing platforms to develop new solutions to find low impact methods of producing textiles.[7]
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Innovations
Nike is changing its policies, and in turn changing the behavior of its suppliers and manufacturers. By offering incentives or administering penalties, Nike is taking a hard line in pressuring its partners to improve social and environmental performance.[8] In FY15, Nike reduced water use by 43% per footwear unit and 18% per apparel unit.[9] Since 2008, Nike manufacturers reduced the energy required to produce a unit of shoes by 50%.[10] Additionally, Nike is making changes to its supply chain operations to reduce costs, and increase sustainability. By converting much of its shipments from air to sea, Nike reduced emissions by over 4% per product, while saving $8M in 2009 alone.[11] The European Logistics Campus is fueled completely by renewable energy, and utilizes the canals to reduce truck emissions.[12]
The Way Forward
As Nike moves forward, it must continue to prove that sustainability and performance are not mutually exclusive. Nike should hold members of its supply chain accountable and continue to encourage innovation from new sources. In an effort to mitigate the environmental risks to its supply chain, some consolidation within regions should occur to exit high risk areas and reduce emissions. Furthermore, increasing the number of products resulting from recycled or sustainable materials have the potential to enable suppliers to be closer to production facilities, resulting in increased efficiency and a diminished footprint. No matter the next move, I anticipate Nike will remain a leader in sustainable innovation.
(800 words)
[1] Doorey, David. Journal of Business Ethics. Nov2011, Vol. 103 Issue 4, p587-603. 17p. DOI: 10.1007/s10551-011-0882-1. , Database: Business Source Complete.
[2] Davenport, Coral. “Industry Awakens to Threat of Climate Change.” The New York Times. January 23, 2014.
[3] Makower, Joel. “Why Nike and MIT see textiles as material to climate change.” https://www.greenbiz.com/article/why-nike-and-mit-see-textiles-material-climate-change. Accessed November 2, 2016.
[4] Makower, Joel. “Why Nike and MIT see textiles as material to climate change.” https://www.greenbiz.com/article/why-nike-and-mit-see-textiles-material-climate-change. Accessed November 2, 2016.
[5] Makower, Joel. “Why Nike and MIT see textiles as material to climate change.” https://www.greenbiz.com/article/why-nike-and-mit-see-textiles-material-climate-change. Accessed November 2, 2016.
[6] Fink, Carly and Whelan, Tensie. “The Comprehensive Business Case for Sustainability.” Harvard Business Review. October 21, 2016. https://hbr.org/2016/10/the-comprehensive-business-case-for-sustainability. Accessed November 3, 2016.
[7] Makower, Joel. “Why Nike and MIT see textiles as material to climate change.” https://www.greenbiz.com/article/why-nike-and-mit-see-textiles-material-climate-change. Accessed November 2, 2016.
[8] Porteous, Angharad H.; Rammohan, Sonali V.; Lee, Hau L. Production & Operations Management. Sep2015, Vol. 24 Issue 9, p1402-1413. 12p. DOI: 10.1111/poms.12376. Database: Business Source Complete.
[9] http://about.nike.com/pages/environmental-impact. Accessed November 3, 2016.
[10] http://about.nike.com/pages/environmental-impact. Accessed November 3, 2016.
[11] Biederman, David. Journal of Commerce (1542-3867). 5/28/2012, Vol. 13 Issue 20, p46A-48A. 2p. Database: Business Source Complete.
[12] Industrial Engineer: IE. Nov2016, Vol. 48 Issue 11, p13-13. 1/2p. Database: Business Source Complete.
Cover Photo: http://about.nike.com/pages/environmental-impact
Nike Ecosystem: http://about.nike.com/pages/environmental-impact



Beyond proving that sustainability and performance could be complementary, Nike faces a great challenge of avoiding a negative consumer reaction on quality given the use of these new technologies. If so, it will be interesting to understand the company’s reactions towards the trade-offs between growth and sustainable innovation.
Great article highlighting the challenges, current innovations and next steps for the business. I agree that as a leader in their field, Nike has an important role to play in promoting sustainable sportswear. A key challenge will be to ‘police’ their existing supply chain to adopt sustainable practices without increasing prices and/or reducing current margins.
I look forward to seeing how Nike achieves scale with their future innovations.