How EA’s FIFA Changed the Game

Electronic Arts’ FIFA is one of the most successful gaming franchises of the last decade due to both the sport’s popularity as well as the developer’s ability to adjust to changing times.
Context – The History of Gaming
Despite tracing its early commercial birth to the 1950s, gaming truly hit the mainstream in the form of the arcade in 1973 with Atari’s release of Pong (see image below). In 1975, the first multiplayer shooter was released and in 1977, Atari released the first at-home console. In the 1980s, the rise of personal computers and advances in computing power propelled gaming forward at an amazing rate. The next major advancement came in the early 1990s with the use of LAN (local area network) parties, which allowed numerous users in a room to connect their consoles together via a LAN and play multiplayer games in large groups. Following the LAN, internet really opened up the world to multiplayer gaming, without the constraints of being physically co-located. Despite some early attempts to capitalize on the internet through gaming in the 1990s, it wasn’t until speeds increased dramatically in the late 2000s that online gaming really took off. The internet brought about the modern age of gaming, connecting users across the globe. According to a recent industry report, “54 percent of frequent gamers feel their hobby helps them connect with friends, and 45 percent use gaming as a way to spend time with their family” (Tech Crunch).
Source: Google Images
EA’s FIFA and The Invention of the Ultimate Team Game Mode
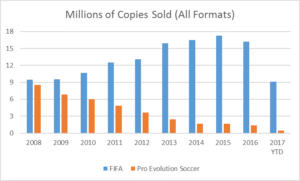
In the late 2000s, there were two major soccer franchises competing on the global scale, EA’s FIFA and Konami’s Pro Evolution Soccer (“PES”, aka Winning Eleven). Market share was tight with many enthusiasts opting for the superior gameplay of PES. That all changed in 2009 when FIFA – in addition to numerous gameplay enhancements made over the years – introduced the Ultimate Team game mode (which EA would add-on to both Madden and NHL franchises in subsequent years) to capitalize on online gaming. See below for a chart of FIFA’s post-2009 dominance.
Source: Created in Excel; data from www.vgchartz.com
Ultimate Team is an online trading card game format. Users compete online against one another using collected player cards to form their individual teams. Users earn coins and other prizes for competing (more for winning) which can then be used to either purchase card packs from the store or to buy individual cards from other users on the transfer market, all with the aim of improving one’s team. The FIFA Ultimate Team (“FUT”) store allows users to buy packs with either coins or real money, a source of added revenue for FIFA. Some users spend hundreds, even thousands of dollars buying packs in an effort to acquire rare players like Real Madrid’s Cristiano Ronaldo. This is in comparison to the game’s retail price of $59.99 for the basic version and $99.99 for the premium version, which includes two free FUT card packs a week.
Source: Google Images
Delivering A Preeminent Digital Product
Not only has FIFA capitalized users’ desire to play and compete with one another online, but it has also augmented the reality of the game through graphics and dynamic player ratings. For example, in the FUT game mode, a limited number of special card versions known as “in form” are released once a week for the players who performed best in “real life” in the most recent week – their “in form” rare card versions include a meaningful ratings boost. This has transitioned into other game modes as well, for example, in the standard game mode, users can choose to play with “live rosters” which include weekly adjusted player ratings based on recent performance. EA provides 24/7 game service monitoring in order to provide these ratings adjustments. Furthermore, FIFA has created a FUT Hub online, allowing users to access, manage, and trade their cards form their computers or smartphones.
EA’s Success in Digital Gaming
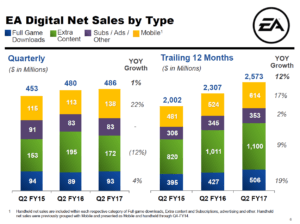
EA has significantly profited from the creation of FIFA’s Ultimate Team and similar digital initiatives. In its recent earnings release, the Company reported $2.6 billion in trailing 12-month revenue from digital channels, $1.4 billion of which is through consoles (where FIFA is predominantly played). The Company, like most game developers, now offers its titles for direct download through consoles rather than selling disks. Of the Company’s $2.6 billion in digital sales, $1.1 billion was from “Extra Content” like Ultimate Team. It is estimated that Ultimate Team game modes from FIFA, Madden, and NHL generate in excess of $650 million annually for EA (and grew at approximately 25%).
Source: Electronic Arts Inc. Q2 FY 2017 Results Presentation
The Challenge of the Future
Despite its recent success, FIFA and its developer cannot be complacent. The advent of virtual reality headsets like the Oculus Rift are poised to disrupt the console gaming market in the future. FIFA’s ability to transition from the living room to headset will determine its success in the next decade.
(781 words)
Sources:
- https://techcrunch.com/2015/10/31/the-history-of-gaming-an-evolving-community/
- http://www.vgchartz.com/
- Electronic Arts Inc. Q2 FY 2017 Results Presentation (November 1, 2016)
- http://www.gamesindustry.biz/articles/2016-03-02-eas-ultimate-team-earning-around-usd650-million-a-year




Thank you for this insightful article highlighting how technological advance has shaped the gaming industry since its inception in 1950s.
I think the gaming industry will be an extremely interesting place for the next few decades given the significant amount of financial resources being invested in Virtual Reality tools, like for example the Oculus Rift you mention in your article. Gaming is often an indication of future applications for new technological innovations. How Virtual Reality will be built into games will likely define the path of how the same technology will be used in the future in other industries, such as telecommunications, retail or even education. It will be interesting to see how companies like Electronic Arts will be able to compete with larger tech companies like Google and Facebook entering the gaming space.
From a more personal perspective, I think that the amount of attention and financial support that is currently being enjoyed by many games manufacturers, poses a certain moral obligation on the gaming industry to develop content that is not only entertaining but also educational to a certain degree. Therefore, I am very interested in how technology will evolve in this space, but also how interactive strategy game manufacturers will develop content for their games in the future.