YouTube – A Super Platform Driven by AI

YouTube is increasingly the most popular video sharing platform in the world, all thanks to Artificial Intelligence!
YouTube is the world’s largest video-sharing platform. Founded in 2005, by Jawed Karim, Steve Chen, and Chad Hurley, YouTube was originally conceived as a platform for these ex-PayPal employees to share their own home videos (Hosch, 2022). Since 2005, YouTube has experienced meteoric growth, going from 30,000 daily views in May 2005 to 2,000,000 daily views in December 2005 to 25,000,000 daily views in January 2006 (Hosch, 2022). In November 2006, YouTube was acquired by Google, but continued to be maintained as its own site. The rest is history, and since the 2006 acquisition YouTube has seen unbelievable success, thanks in large part to their strategic and innovate use of artificial intelligence (AI).
Originally conceived as a site for amateur home videos, YouTube has steadily become one of the most important distribution channels for all types of content. Whether it’s educational, gaming, cultural, or company specific-content, YouTube offers a unique platform for all types of videos. Platforms are powerful, and YouTube is no different. It has amassed its unique position as a leader in video content through much organic growth coupled with AI-based technology to augment its offerings. YouTube is a unique platform with AI central to its value offerings.
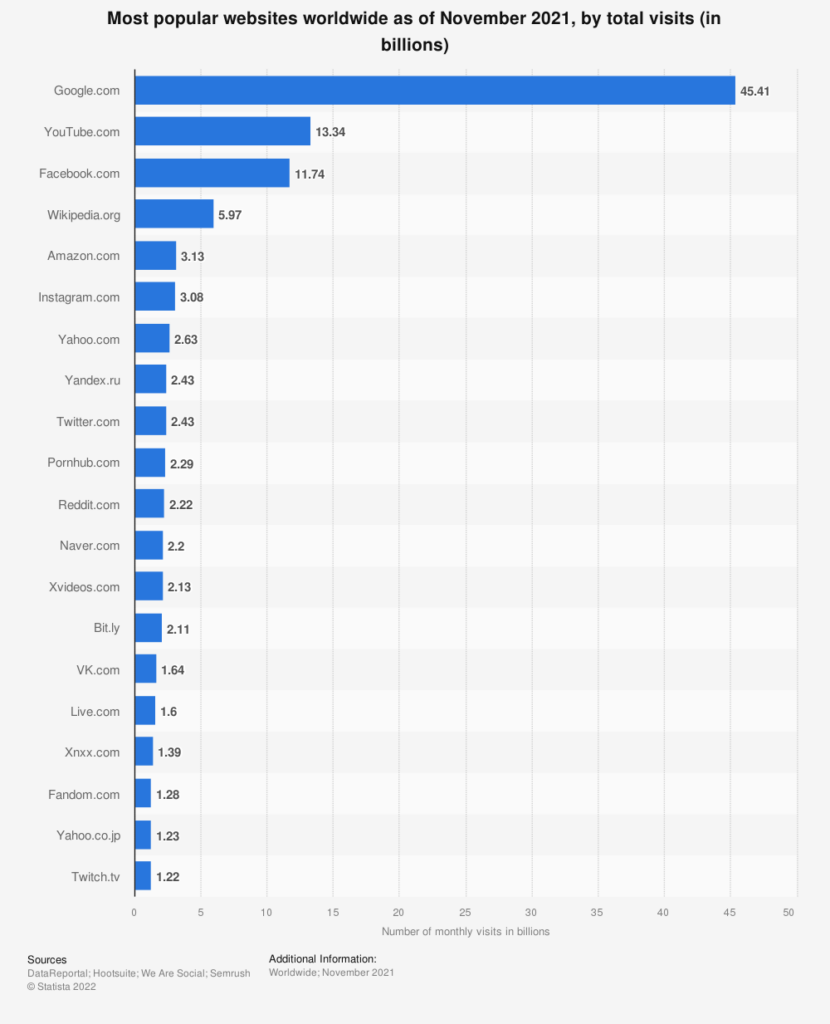
As of November 2021, YouTube was the second most visited site in the world with 13.34 billion visits per month. Second only to Google, which receives a whooping 45.41 billion visits per month, YouTube is increasingly one of the most visited websites out there.
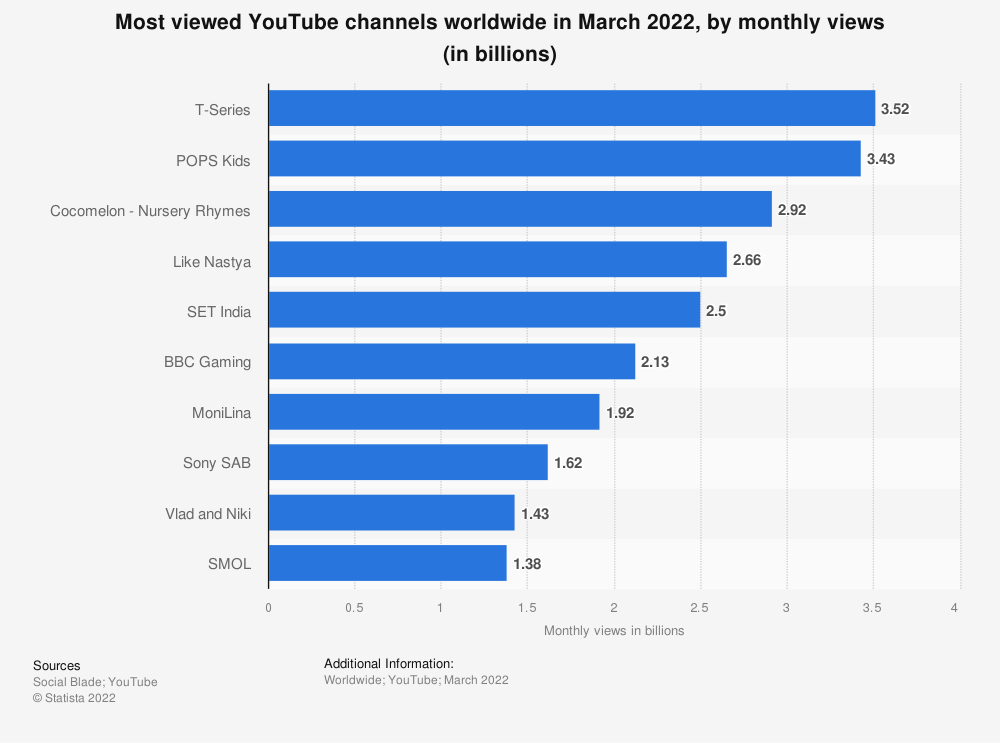
As mentioned above, YouTube offers a huge range of content on its platform. Below, you can see the most popular YouTube content by monthly views. T-Series, an Indian music and film company, has the most monthly views with around 3.52 billion views. T-Series immense popularity speaks to the popularity of YouTube in India. As of 2022, India is the country that houses the largest YouTube audience with over 460 million users engaging with the platform (Ceci, 2022). For reference, the United States is second with over 240 million YouTube viewers.
Closely followed by T-Series is POPS Kids, a leading educational and entertainment provider for kids. The fact that POPS Kids and T-Series are so close in their monthly views (both over 3 billion!) speaks to the breadth and depth of YouTube’s offerings. YouTube is truly a platform with a diversity of offerings. However, the content itself isn’t just the value that YouTube offers, the value also lies in how YouTube surfaces and recommends content.
One of YouTubes biggest value offerings beyond the content istslef is the recommendations and curation for suggested videos. When a user first opens up YouTube, they are greeted with a familiar page with new videos. These videos are called recommended based on AI-algorithms. After a user watches a video, they are created with another page of recommended videos. Many users who frequently go on YouTube, including myself, rarely search for videos. Instead, YouTube’s algorithms are so thorough that they are able to drive the viewing experience.
YouTube is able to achieve its terrific recommendations through a two-facing AI algorithm. One component of the algorithm is the candidate generation, and the other component is the ranking network. Candidate generation involves understanding the user’s history and comparing a user’s history with other users’ key information such as how many and the types of videos watched, as well as demographics. The ranking network, “uses a ‘rich set of features describing the video and user’. This two-tiered system allows the system to handle millions of videos, but also scale down to individual users and provide them with meaningful content” (Anderson, 2019).
The ranking system is particularly important as YouTube receives thousands of new videos uploads every day, and YouTube only wants to recommend high quality videos. To know which videos are high-quality, YouTube measures the time that users spend watching videos as a proxy for the quality of the videos. AI algorithms then use that data to make predictions based on a user’s history how likely they are to watch a video. As Anderson notes, this is achieved through, “weighted logistic regression. The reason it is weighted is that only positive videos are given weight. A positive video is where a user has actually clicked on the video at all, this helps the algorithm learn only about videos that the user interacted with” (Anderson, 2019). Both the candidate generation and ranking network are central to YouTube’s value creation.
YouTube also utilized AI when they rolled out a feature for adding ‘chapters’ to videos. This novel feature allows users to see clips of videos before watching them. For example, a user would hover their mouse of a video they want to watch and the ‘chapters’ would begin playing. In a blog post, Jordan from YouTube wrote,
“We want to make it easier for people to navigate videos with video chapters, so we are experimenting with automatically adding video chapters (so creators don’t have to manually add timestamps). We’ll use machine learning to recognize text in order to auto generate video chapters” (Jordan, 2019).
This machine-learning enabled innovation makes it easier for creators to upload videos without choosing a specific timestamp, and it allows viewers to gain a ‘sneak peek’ into the content
Nearly 14 years after YouTube’s acquisition, a global pandemic changed YouTube’s operating model and principles. The demand for work-from-home coupled with a rise in misinformation and violence from the pandemic catalyzed YouTube’s innovative use of AI to filter and censor videos. In August of 2020, a few months into the pandemic, YouTube leveraged AI to remove 11 million videos from its site (Narayan, 2020). These videos contained misinformation or violence, and 10.85 million of them were flagged by YouTube’s AI bots. YouTube continues to leverage AI to flag videos for removal.
Overall, YouTube is an increasingly popular platform for video sharing, and AI is central to their operating model. Whether it’s predicting cat videos, teaching kids how to do math, or a ‘how to video’ about installing gutters, YouTube is the go to place for high quality video content, all thanks to Artificial Intelligence!
References
Ceci, L. (2022, January). YouTube users by country 2022. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/280685/number-of-monthly-unique-youtube-users/ DataReportal. (2022, January). Global top websites by monthly visits 2020. Statista. https://www-statista-com.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/statistics/1201880/most-visited-websites-worldwide/ Hosch, W. L. (2022, March). YouTube | History, Founders, & Facts | Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/YouTube published, R. N. (2020, August 27). YouTube uses artificial intelligence to remove 11 million videos in a quarter. TechRadar India. https://www.techradar.com/in/news/youtube-uses-artificial-intelligence-to-remove-11-million-videos-in-a-quarter Rangaiah, M. (n.d.). How is YouTube using Artificial Intelligence? | Analytics Steps. Retrieved April 17, 2022, from https://www.analyticssteps.com/blogs/how-youtube-using-artificial-intelligence Social Blade. (2022, March). Most viewed YouTube channels 2021. Statista. https://www-statista-com.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/statistics/373729/most-viewed-youtube-channels/



Hey Maxwell, thanks so much for your great post. As I was reading it, I couldn’t help but notice how many new AI features YouTube have added that have created so much value.
I have noticed that through the years I have relied more on watching recommended videos rather than searching for videos to watch.
I also had no idea that the chapter feature is sometimes auto-generated! Whenever I’m watching a Youtube video without chapters included, I am always very frustrated and I tend to blame the creator for not taking care in including such a useful features. What a great idea it is from YouTube to use AI to auto-generate video chapters.
Loved this read. Youtube’s algorithm that generates content based on the candidate information and the network information has been an area of interest in my work with students. More than half the computers in the K–12 market in the U.S. are Google Chromebooks that usually come preloaded with YouTube. Understanding that engagement is a core part of the Youtube business model, the dark side of the issue is that users often receive recommendations for noxious material because it is considered engaging and it is borderline content but it unfortunately misinforms and causes harm. Although Youtube is using AI to remove harmful videos, it still has so much work to do and I wonder if the mounting pressure from the public will actually force Youtube to open their algorithm to external scrutiny.