The future of Harvard Business School Online: Disrupting or being disrupted?

As many industries suffer from COVID 19 namely retail, restaurant, hotel, transportation, and travel, some, including online learning, have seen a tremendous growth during the crisis. One online learning platform that we will examine closely is Harvard Business School Online Learning (HBS online).
Founded in 2014, HBS online, originally named “HBX,” is Harvard Business School’s attempt to venture into the online learning world with the goal of making business education more accessible, while ensuring the venture remains financially sustainable. Since HBS changed the name of the platform, there has been approximately 70% immediate uptick, signifying the importance of the legacy and Harvard Business School’s brand name.
What is Harvard Business School Online?
HBS online simulates the famous Harvard Business School pedagogy case-study method in its “HBS online live” platform, a virtual classroom that enables real time interaction, and the famous “cold-calling” that is brought to life in an online learning setting. This online learning product mainly targets executives. In addition to “Live,” the core product, HBS Core (Credential of Readiness), which offers: Business Analytics, Economics for Managers, and Financial Accounting, positions itself to serve undergraduates and students majoring in the liberal arts, which will find the business fundamentals helpful for their career preparation, as well as students deciding whether to pursue an MBA degree full-time or those who need the basics before enrolling at a 2-year MBA residential program.
To date, approximately 40,000 students that have experienced HBS online—keeping in mind that these numbers represent full-paying customers. In five years, unlike many of its competitors, HBS has reached financial sustainably and generated a modest amount of surplus in order to expand its mission to make the MBA education more accessible.
The platform yields strong network effects both same-side and cross-side. The same side network effects can be seen as HBS online creates a community of instructors who derive great value by offering their teaching to a wider global talent pool. Given that entry into the HBS MBA program is such a selective process, this platform creates the opportunity to provide learning opportunities to a wider audience. For the students, the attractiveness is the value of learning with students from a diverse, global community and network that would otherwise be difficult to access and join. The cross-side network effects also apply in that the more courses HBS online offers, the more students the platform can attract and the more faculty engagement is created with students who can benefit from being part of HBS online’s learning environment.
HBS online’s response to COVID 19
Deepening existing relationships
In times such as COVID 19, Harvard Business School, as a leading global higher education institution, is challenged, in new ways, to fulfill its responsibility to society. HBS online is well positioned to respond and help with this crisis. HBS online turned the crisis into an opportunity to deepen the school’s existing relationships with 30 collaborating colleges and universities reaching more than 50,000 students to have students access to the course. HBS online also brought down its price for CORE (Credential of Readiness) from $2,250 to $450, making it more affordable, and thereby decreased the financial burden for students.
Exploring new opportunities by giving free offering
Apart from offering a lower price point to community colleges and universities, during the crisis, HBS online made some of its course offering free. Within 2 days, HBS online had over 36,000 registrants and had to immediately limit enrollment because it exceeded HBS online’s technical capacity and the ability to run the course as designed, given that it is intended to involve cohort learning. The HBS online experience is interactive, cased-base, and participatory.
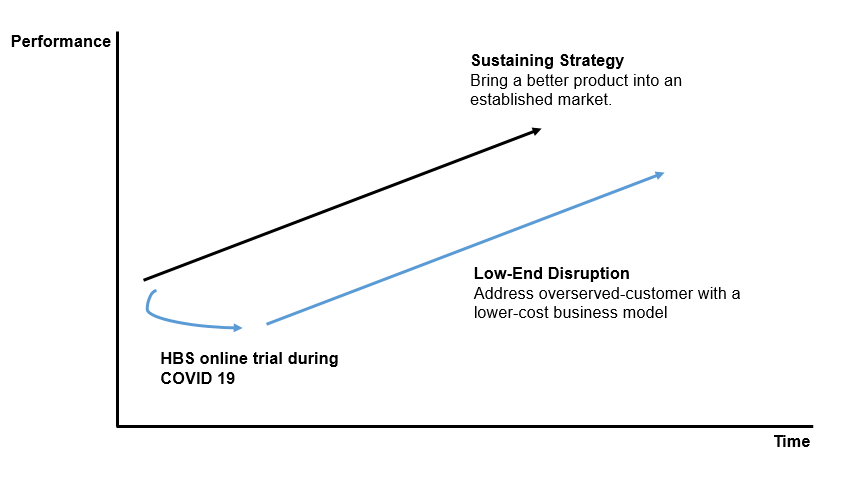
How will this impact HBS online in the long-term?
As we all become familiarize with online education during this COVID 19 time, we can expect that online learning will not only increase in terms of numbers of users but also attract new entrants to the market.
We can anticipate a disruptor in the market that will seize the opportunity in the low-end market like some of the 36,000 registrants who flocked to HBS online’s free offering.
The investment market is also becoming more interested in the education technology sector, with a surge of investment in particularly in markets such as China and India. We’ve also seen more dollars enter the education technology market in the US due to this crisis, which turned the spotlight on remote online learning solutions, a previously high risk and unattractive market.
Recommendations to sustain HBS online’s growth
New user segment
COVID 19 presents an opportunity for HBS online to engage with the unemployed, projected by the ILO to be over 190 million world-wide due to the crisis. There are opportunities to reach an untapped market, however consideration of societal impact is warranted here.
Knowing that HBS online strives to also have a strong financially sustainable model, contributing to the unemployment sector to could help improve employment and career opportunities. As a result, a population that otherwise might not be able to avail itself of this knowledge, could potentially become main contributors and long-term users of the HBS online platform going forward.
In order to maintain HBS online financial health and at the same time serve a new demographic, HBS online should explore partnering with government, colleges, and universities to explore the possibility of becoming part of the solution to ease the job loss impacts.
HBS online’s leadership to drive societal impact on being part of the workforce upskilling is greatly called for.
Product innovation
Digital transformation and automation have become a mandatory competency that firms should have. Given the current crisis, companies will accelerate their timeline to transforms themselves. In order to keep up with the pace of change, HBS online will have to reevaluate the course offering to meet the demands of the industry. For example, in addition to the CORE platform, HBS online should consider offering courses in technology and innovation to increase not just business but also, technology literacy. Harvard Business School can leverage the MSMBA program, the joint Engineering Master and Business Management program faculty resources to make its offering relevant and competitive.
In addition to content, in order to accommodate a large number of students and be responsive, HBS online can explore building an intelligent virtual assistant to help with frequently ask questions and course navigation, which will help enhance and personalize the learning experience.
Strategic Alumni engagement
Unlike other online offerings, HBS online differentiates itself both on the pedagogy and also the community aspect, which, to an extent, emulates the in-person MBA residential experience. There are 85,000 alumni in 169 countries. This is an unparalleled and untapped potential pool of talent that could be useful in HBS online course construction with relevant industry related insights. Many HBS alumni are leaders in their respective sectors. This is also an opportunity to build value that will also help attract more customers to use the platform drawing from the extensive network and expected insights from HBS alumni who hold senior leadership positions in their respective industries.
International expansion
Seeing the growth of US universities and colleges, HBS online should accelerate its partnership with international universities. As online learning becomes more and more competitive, and the barrier to entry into this space will become easier with change in user-behavior (as the world becomes more accustomed to online learning) and the untapped scale that online learning can provide. Being one of the first players to establish relationships internationally will help create a competitive positioning for the HBS online This also aligns well with HBS online core mission to make the MBA education more accessible. 34% of the MBA class is international, which already indicates how the HBS brands holds weight globally.
Risk and mitigation
As HBS online continues to innovate beyond the basic business fundamentals, to courses that that are more similar to the offering in a 2-year MBA residential program experience, HBS might risk that potential incoming students could find the online experience sufficient. Although this might be true, it will only apply to students who put less value on the MBA degree as HBS online doesn’t grant degree or any credentialing.
In addition, it could be argued that making HBS online more accessible could taint the exclusivity of the brand. This may cause those who are paying the full 2-year MBA price to think about alternative ways since they can also gain crucial business knowledge online.
However, is not very likely. The MBA itself is highly competitive, with acceptance of 10%/ year. Maintaining the accessibility through HBS online can only help since the two offerings are different in its experiences, and will continue to attract those who want to invest full-time versus those who would want a shorter term upskilling offering.
In order to keep the programs separate, it will be important to distinguish the communities, so that each serve different purposes: With the HBS online, making sure that there are immediate transferable skills, and maintaining the MBA program as a more immersive, exploratory and self-discovery mode of learning.
With many competitors in the market offering business related topics, for example coursera, edX, Udacity, Udemy, there is a clear risk of multi-homing (the same users using multiple platforms), and the switching cost is low for the online offering both free and paid. HBS online might need to consider how to improve the lifetime value of the platform for its users for example, consideration of a subscription model, discount with purchase pf multiple course offerings, broadening access to personal interaction with professors for users who are power users (those who frequently used HBS online). These are just preliminary examples to consider, however, as online learning become increasingly competitive, it will also be easier to access by individual instructors, who might utilize platforms like Zoom to conduct their own courses. HBS online will have to think more seriously how to retain its customers long term by creating more community interaction, and have users feel the sense of unity, which is what the HBS MBA program does well and which could be a model to apply to HBS online.
The quality of both instructors and also students in the platform will also be crucial as the platform has strong network effects, HBS online will have to balance the ability to make the courses accessible and the ability to develop a selection process that will help screen for those who help foster a strong learning community. Ways to approach this could include providing more robust assessment at the end of the course to ensure that the students who graduate from the course have a level of understanding and skills that the course requires, and also measuring learning engagement along the way to ensure active participation that will help foster a positive learning environment with its learners community.
Since COVID 19 has demonstrated the possibility of how the 2-year MBA experience could also be executed online, the important thing for HBS online is to constantly reevaluate its strategy and positioning, since the market could be shifting, and it might be important to design with that in mind, making sure both HBS and HBS online are listening to their students.
References:
Increase in HBS online enrollment
HBS online will keep changing the game
Photo credits: Harvard Business School online





Thanks for an interesting blog post Viria! I think HBS Online is in a tough spot. Even if they were to see an increase in uptake during the pandemic while they offer courses for free or a discounted price, I think they need to work on customer segmentation and adjust their course offerings and messaging accordingly to make it sustainable.
Their current target customer groups appear ambiguous – are they trying to target young students aspiring to get into b-school and want a taste of what HBS is like? Or mid-career professionals looking to upskill to get promoted within their organization? Or mid-career professionals looking to reskill and transition to new jobs? Or anyone who can afford the hefty prices and just do it for fun, out of intellectual curiosity? When you look at their current course offerings, apart from a select few (e.g. accounting, finance, and business analytics), the courses are not technical enough to offering meaningful upskilling/reskilling, so those who are seeking to hone their technical skills will likely go to Udacity, Coursera, etc. In this sense, I would assume that most customers are coming primarily for the ‘brand’, rather than necessarily skill acquisition. If that’s the case, perhaps they should add more courses with big names and/or unique courses that focus more on soft-skills. Also, given the price tag, they should work more closely with B2B customers, for example offering group discounts to companies.