Globalization with Apple

If the cost of manufacturing continues to increase in China as predicted, will it continue to be the best place to manufacture for Apple products?
Apple Inc has received a lot of bad publicity for using Chinese manufacturing companies to build most of their products. As a consumer would you be willing to pay at least $100 more for an iPhone to know it was designed and manufactured in the United States? (1)
Apple’s role with International Trade
Apple along with other manufacturing companies has taken manufacturing overseas to reduce costs and improve efficiencies. Many of the upstream components and subassemblies are also manufactured in China and Southeast Asia, so to do final assembly in the United States would create huge logistical challenges. China also has much larger and more nimble factories than in the United States. (2) Labor is starting to become an issue during peak seasons, usually over the summer due to the large number of manufacturing companies looking for labor. Companies are competing for moderately “skilled” labor to meet the demands of product launches. During an iPhone launch contract manufacturers need to hire or re-allocate around 250,000 people to work on finally assembly of the new iPhone. There are also all of the upstream suppliers who are also in need of employees to work on their sub-assemblies and components that go into the finished good. Apple now pays a premium on top of minimum wage to their contract manufacturers to ensure that they receive the labor needed to not delay production. Even with China’s population it is still a challenge to meet the demands of labor when so many companies are competing for the labor. Apple is currently heavily weighted in China for final assembly manufacturing, but if there were any changes in government regulations or tariff rates as stated by President Trump, it could put Apple at a significant disadvantage to getting product to customers in a timely manner and take an enormous hit to margins. (3)
Apple’s current strategy
Apple has done a lot for the United States economy and unemployment rate other than moving jobs overseas. For the short term Apple has created a lot of jobs within the United States outside of manufacturing its hardware products. Apple has many other areas of business where it has created jobs within Apple and the rest coming from suppliers and developers. Apple has created over two million jobs within the United States and has spent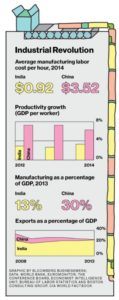 over $50 billion with US suppliers. (4)
over $50 billion with US suppliers. (4)
For the mid term, Apple has started to look at other countries to do their final assembly production. Apple is looking to produce in other countries, not just to reduce costs but to also increase revenues. IPhone market share in India isn’t in the top five smartphones so there is a large opportunity to establish its brand with the worlds 2nd largest populated country. (5) India is a strong candidate because the labor wages are approximately 25% the cost of labor in China, they have the experience and skill to quickly learn the manufacturing process for iPhones, and they have the ability to keep up with labor demands during peak seasons. (6)
President Donald Trump and Apple CEO Tim Cook met to discuss Apple’s future of manufacturing overseas. President Trump claims that Tim Cook has promised to build three large plants in the United States. Apple continues to explore its options of where to manufacture based off of costs, complexity, potential and capability. Producing in the United States poses other risks such as speed to market, increased costs, and manufacturing flexibility.
Recommendations for Apple
I think the Apple management team should make a bigger effort to explain the benefits of manufacturing overseas other than costs. Benefits include international opportunities to its employees, speed to market for its customers to have the latest and greatest technology, and efficiencies in the supply chain with the sub-component suppliers. Apple should also promote the number of foreign workers they have sponsored to work in the United States to add to the country’s diversity and accomplished population.
I also think that Apple needs to ban together with other manufacturing companies such as Microsoft, Alphabet, and Amazon to contest the current President’s goals of bringing all manufacturing back to the United States and “making America great again”. To bring that much manufacturing back to the United States would be a drastic change that would cause the companies to invest a significant amount and money and resources toward the move back and the country may not be able to keep up with the high demands of skills and labor needed to produce all hardware products.
Key Outstanding Questions
- With the rising labor costs in China and the competition for labor should Apple consider moving back to the United States or to another country? If so, which country?
- Do you think the United States can handle bringing back all manufacturing jobs in the medium term?
(Word Count 798)
End Notes
- Swearingen, Jake. “Apple Isn’t Building 3 Factories in the U.S., No Matter What Trump Says.” Nymag.com, 25 July 2017, nymag.com/selectall/2017/07/despite-trump-claims-apple-wont-build-3-factories-in-u-s.html.
- Blodget, Henry. This Article Explains Why Apple Makes iPhones In China And Why The US Is Screwed. Business Insider, 22 Jan. 2012, businessinsider.com/you-simply-must-read-this-article-that-explains-why-apple-makes-iphones-in-china-and-why-the-us-is-screwed-2012-1.
- Kharpal, Arjun. Apple is exploring moving iPhone production to the US: Report. CNBC, 18 Nov. 2016, cnbc.com/2016/11/18/apple-is-exploring-moving-iphone-production-to-the-us-report.html.
- Apple CEO Promised to Build 3 ‘Big’ Plants in U.S., Trump Says. Fortune, 25 July 2017, fortune.com/2017/07/25/apple-ceo-big-plants-trump/.
- Vincent, James. Apple has started assembling iPhones in India. The Verge, 17 May 2017, theverge.com/2017/5/17/15651842/apple-iphone-india-assembling-begun.
- Zhu, William. Comparison of Manufacturing Between India vs. China. LinkedIn, 9 Sept. 2016, www.linkedin.com/pulse/comparison-manufacturing-between-india-vs-china-william-zhu/.



I agree that it is not viable to bring a great deal of labor-intensive manufacturing back to America. The cost seems too high for most companies and would ultimately be passed through to the consumer. I think a better approach is understanding the root causes that are driving companies to manufacture abroad (e.g., is it purely cost of labor or other factors). The New Yorker posted an interesting article about Trump’s manufacturing policies (see link below). I believe the labor content required for manufacturer is going to decrease while the need for skilled workers who can operate specialized manufacturing equipment will grow. Both the US government as well as US based companies like Apple should evaluate how they are positioning American workers to shift to the changing environment and help these employees receive the requisite training they need to handle the shift to the modern factory.
https://www.newyorker.com/business/currency/why-donald-trump-is-wrong-about-manufacturing-jobs-and-china
Although the future of unskilled or low-skill labor seems very much in question, this article also brings into question the very long-term implications of new technology and the effect on capital and labor investment. If machines/capital are able to replace more and more human labor, will the production shift back to the countries where the final goods will be sold? Or will it still make sense to manufacture those items in certain countries based on the labor base and the price of the labor in those countries? Furthermore, what affect will the shift from human labor to capital for production have on those countries that have relied heavily on manufacturing jobs to boost the middle class?
Very interesting topic!
There were two things that came to my mind as to how apple can combat wage inflation.
1. Automation: How much will Apple invest in automation and work with their suppliers to reduce dependency on labor, especially eliminating the low to medium skill jobs. However, this is not easy and will take time.
2. Diversification of supplier base: Given the need to expand the manufacturing footprint and move to cheaper locations, India is a potential destination for apple with one of the solutions being to manufacture the older iPhones in Bangalore [1]. Yet, developing new suppliers and maintaining quality and scale in India is a whole new challenge.
However, on the isolationist policy and moving manufacturing back to US, Apple could potentially move manufacturing of some of the low volume high complexity items to US, employing few workers as a show of good faith. But with regards to scale and cost, I am unable to see how they would ever be able to manufacture a large portion of their demand in the US.
[1] http://mashable.com/2017/03/24/apple-iphone-india-6-6s-se/#Q9i1Fz2vCsq2
Thanks for sharing your insights on Apple and the implications protectionists policies will have on the company moving forward. To answer your first question regarding Apple’s response to rising labor costs in China, I do think that in the short term Apple should consider diversifying its geographic footprint to expand into neighboring countries with lower labor costs. That being said, I believe increasing dependence on automation will have a tremendous impact on Apple’s strategy moving forward as it considers labor costs management. As more and more workers are replaced with machines, Apple prospects of moving manufacturing back to the US in line with Trump’s protectionists agenda may increase. I think the central question to answer here is what type of labor Apple will need from a manufacturing prospective in the automated landscape of the future.
Lastly, I think one other element that will figure into Apple’s decision to invest more in US manufacturing is where its key partners and suppliers are going. Foxxconn, one of Apple’s largest manufacturing partners, already has plans to build new factories in the US [1], and if this trend continues I believe that Apple may consider increasing their US investment as well.
[1] https://www.cnbc.com/2017/05/09/foxconn-us-factory-likely-may-be-used-for-iphone-and-ipad-displays.html